Table of contents
Type casting is a process to convert a variable datatype to another variable data type.
Let's see two types of conversion that are implicit and explicit.
Implicit is conversion in which a variable is converted automatically by Python, whereas an explicit conversion is converting based on user requirements.
For example, int () converts the data type to an integer variable and str () converts the data type to a string variable.
Typecasting the input to an integer
if you get a requirement to convert integer input from the user, below is an example that takes two inputs from the console and types cast them to an integer value to print the sum.

User Input - Multiple user inputs
In Python multiple methods are available but we will see an example of using split() method.
split() methods help get multiple inputs from the user and break the input by a specified separator. If in case separator is not provided then any while space is a separator.
split () method is used to split a Python string and it can be used in multiple inputs let's see an example.

Python Output - print()
print() function prints the message to the screen.
syntax : print(value(s), sep= '', end ='\n', file=file)
Parameters
value(s)= value that can be converted to a string before printed
sep= 'separtor'
end: 'end'
file: an object with a write method. defualt :sys.stdout
return type: it returns output to the screen
example:-
print (a,b,c,spe="_")
print (" python for devops", end="**")

Another example of split method by storing the value in .txt file


One of more Output method - format() method
format () method helps us to concatenate the elements within an output through positional formatting.
for an exmple
# using format() method
print ('welcome to {} for "{}!"'.format (Python','devops training'))
we will use above image program and change with format () method to demonstrate .

we can even print the value with indexing like below

Variables
Note :- variables are a like container to hold the values and the naming conventions must be meaningful that describe the value it holds
Local Variables
Local variables scope is within the function like the below example
def addsum( firstnum, secondnum) # function defined
sum = firstnum + secondnum
return sum
here ( firstnum, secondnum) is accessible within the function
Global Variables -
it is defined in the main body of the program outside the functions. global variable accessible in the entire program.
a = int(2) -- a global variable
b= int (3) -- a global variable
def addsum( firstnum, secondnum)
sum = firstnum + secondnum
return sum
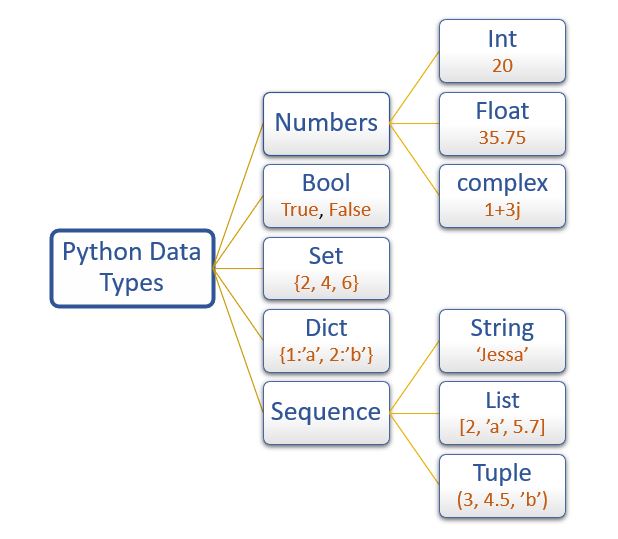
Data types:-
Integers - accept integer value ( 3,45,34)
float - accept value in digits (1.3,3.4,4.4)
complex - combination of real and imaginary ( 3 +7j) or (3i + 7j)
strings - string value " enter your value"